AWS CloudFormation
In the consecutive weeks of ten and eleven, we have leveraged the power of Infrastructure as Code to provision and manage the main components of the app with the design to wrap up the bootcamp¹, easily manage updates to the application services², maintain consistency³, and enables the automation of the deployment process⁴ when needed.
Week Ten Main Tasks
What is AWS CloudFormation?
CFN is a powerful IaC provided by AWS. It allows you to define and provision your cloud infrastructure using declarative templates either in JSON or YAML format as is the case for our scenario. These templates describe the desired state, including resources, configurations, and dependencies in a very readable code.
CFN Full Asset (opens in a new tab)

State Management
In CloudFormation, state management is handled differently compared to IaC tools like Terraform and Ansible, explore the key differences below.
| CloudFormation | Terraform | Ansible | |
|---|---|---|---|
| State | Managed internally by AWS | Local state file | No explicit state file |
| Approach | Immutable infrastructure | Mutable infrastructure | Idempotent execution |
| Stacks | Yes | No | No |
Provision First Project
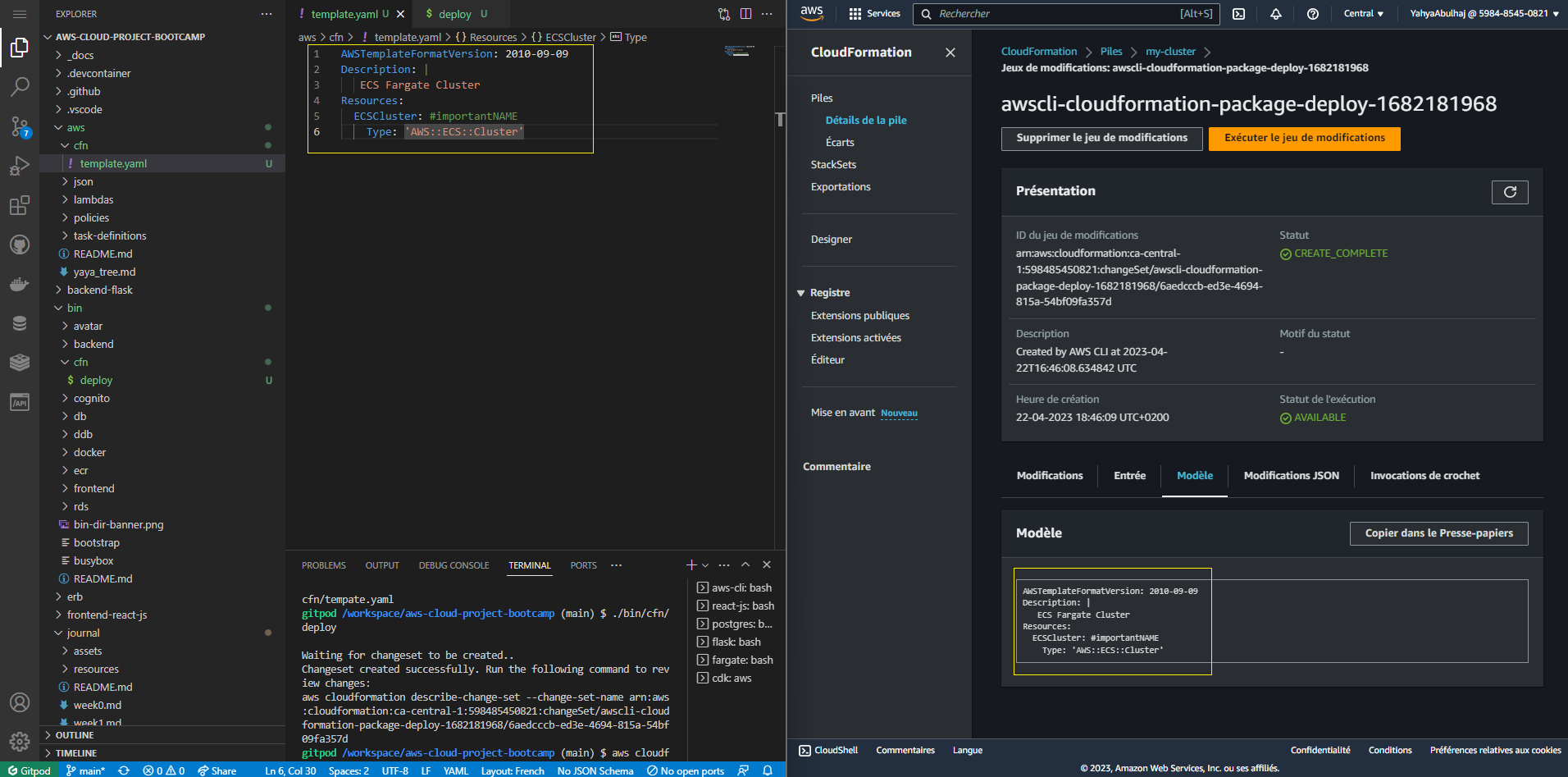
Let's get you going with a simple provision of a Cluster.
- Create a file in a given direcotry and name it
template.yaml - Specify the header for
AWSTemplateFormatVersionand addDescription
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: ECS Fargate Cluster- Define the resources you want to create using AWS, we said ECS Cluster:
Resources:
ECSCluster: #LogicalName
Type: 'AWS::ECS::Cluster'- Specify any additional configurationsas needed e.g. security groups, IAM roles.
- Create Bucket for the template artifact
aws s3 mb s3://cfn-stuff-goes-here- Set your environement variables for
$STACK_NAME,$BUCKETand your AWS$REGIONe.g.
export BUCKET="cfn-stuff-goes-here"
export CFN_PATH="<path-to-ur-template>"- Authenticate and deploy using AWS CLI.
aws cloudformation deploy \
--stack-name $STACK_NAME \
--s3-bucket $BUCKET \
--s3-prefix cluster \
--region $REGION \
--template-file "$CFN_PATH" \
--no-execute-changeset \
--tags group=best-cluster \
--parameter-overrides $PARAMETERS \- Navigate to the AWS Management Console and manually execute the changeset to initiate the provisioning of the infrastructure.
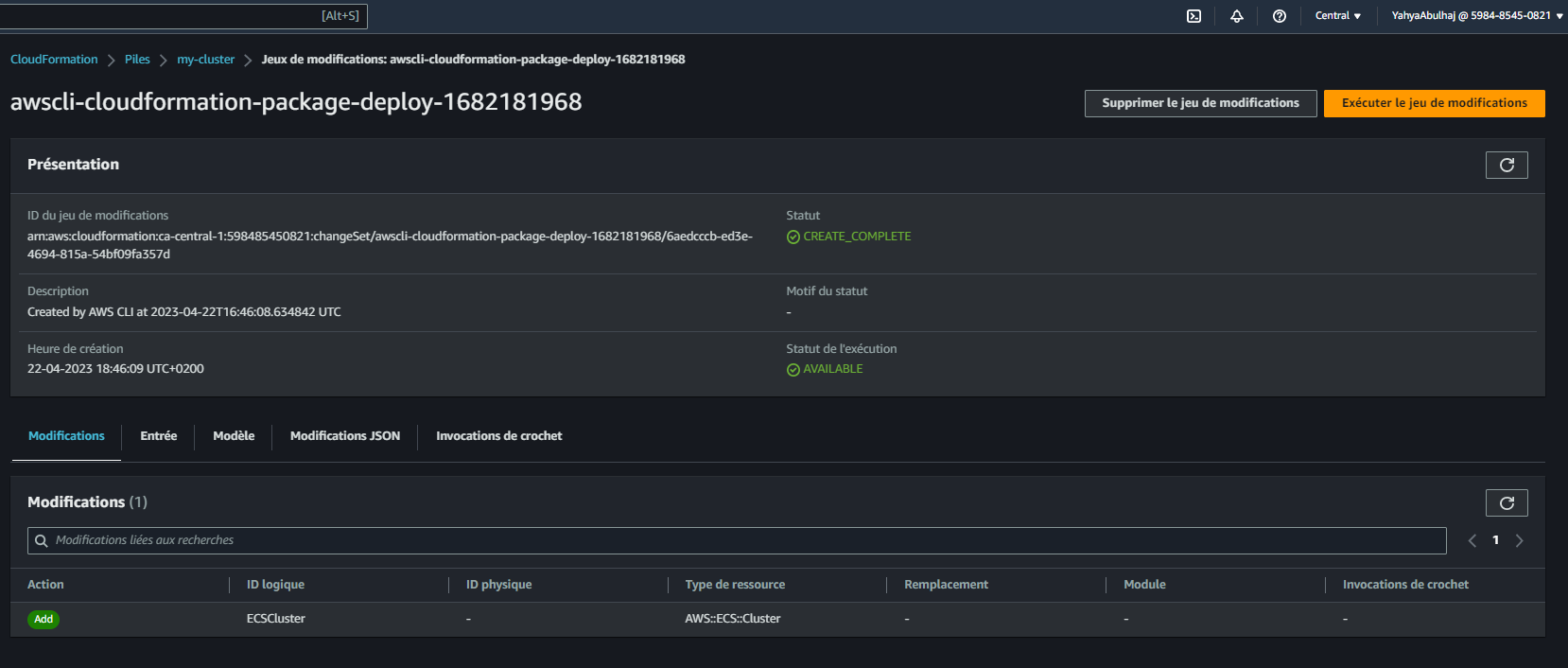
The inclusion of this manual execution step using the --no-execute-changeset \ flag is done for security reasons, ensuring that critical changes to the infrastructure are carefully reviewed and approved before being implemented.
Beyond the workflow, the key aspect of working with CFN lies in developing robust and secure templates.
Check Project Templates
CFN — Policy As Code
This is an approach that involves expressing and managing policies in the form of code.
During CFN Implementations, It is as important to enforce compliance and PaC helps ensure that the deployed infrastructure adheres to the organization's policies and standards.
Application CFN Guard
CFN Guard allows us to define custom rules and policies that are enforced during the CloudFormation stack deployment process. This ensure that our infrastructure deployments comply with security, compliance, and governance requirements.
To get start with CFN Guard and leverage capabilities for validating your (CFN) templates, follow these steps:
-
Install Rust (opens in a new tab) and Its PM Cargo.
-
Get Guard from Cargo
cargo install cfn-guard- verify that CFN Guard is successfully installed by running the command
cfn-guard --version- Create
task-definition.guardfor our cluster. - Apply it against a temlpate
cfn-guard rulegen --template /workspace/awsbootcampcruddur-2023/aws/cfn/template.yaml
- Inlclude the rule value to
aws/cfn/ecs_cluster.guard. - Validate the CFN template
cfn-guard validateCFN validate
This tool helps prevent common security risks that could potentially impact your infrastructure. Ensuring the templates are well-formed and follow the recommended CloudFormation syntax, reducing the likelihood of introducing vulnerabilities or misconfigurations.
To validate a CloudFormation template, you can use the below command
aws cloudformation validate-template --template-body <value> [--template-url <value>]--template-bodyor-t: Specifies the CloudFormation template to validate, either as a string or a file path. You must provide either--template-bodyor--template-url.--template-url: The URL of the CloudFormation template to validate. You must provide either--template-bodyor--template-url.
aws cloudformation validate-template --template-body file:////path/to/your/cfn/template.yamlAWS CloudFormation will examine the syntax and validate the contents of the template. If any errors or warnings are detected, they will be displayed in the command output.
Another potential tool to validate your CFN is taskcat (opens in a new tab)
CFN Lint
Cfn-lint is tool that provides linting capabilities for CFN templates to identify and address potential issues, errors, and security risks.
Integrating cfn-lint into your preferred IDE is a breeze. Simply install it using this command
pip install cfn-lintRunning linter Just execute the command to analyze your CFN template and receive valuable feedback.
cfn-lint <path-to-template> TOML and Config Management
Another thing that you may employ is the TOML, The obvious config Language built by the multi-billionaire and GitHub CEO Tom for storing configuration data and make It change consistent and agile to config.
- Make sure you have
Rubyand installTOMLfromGem
gem install cfn-toml- Create a new file
aws/cfn/cluster/config.toml
[deploy]
bucket = 'cfn-artifacts-111'
region = 'us-east-1'
stack_name = 'CrdCluster'
[parameters]
CertificateArn = 'arn:aws:acm:<region>:<aws-id>:certificate/8a62223d-469e-4094-8c9d-bbecb01bba5d'
NetworkingStack = 'CrdNet'- Pass the parameters to
bin/cfn/clusterscript
#! /usr/bin/env bash
set -e
CFN_PATH="/workspace/aws-cloud-project-bootcamp/aws/cfn/cluster/template.yaml"
CONFIG_PATH="/workspace/aws-cloud-project-bootcamp/aws/cfn/cluster/config.toml"
echo $CFN_PATH
cfn-lint $CFN_PATH
# TOML Zone
BUCKET=$(cfn-toml key deploy.bucket -t $CONFIG_PATH)
REGION=$(cfn-toml key deploy.region -t $CONFIG_PATH)
STACK_NAME=$(cfn-toml key deploy.stack_name -t $CONFIG_PATH)
PARAMETERS=$(cfn-toml params v2 -t $CONFIG_PATH)
# TOML Zone
aws cloudformation deploy \
--stack-name $STACK_NAME \
--s3-bucket $BUCKET \
--region $REGION \
--template-file "$CFN_PATH" \
--no-execute-changeset \
--tags group=cruddur-cluster \
--parameter-overrides $PARAMETERS \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM- Run the bash script file
./bin/cfn/cluster-deployto fetch from Toml.
To learn more about TOML and how to leverage it effectively, refer to my previous work with SAM available here.
TIP: You can streamline the installation of cfn-lint, cfn-guard, cfn-toml in your gitpod.yml.
OWASP Infrastructure as Code Security Cheatsheet (opens in a new tab)
Yacrud CFN Stack
The architecture diagram showcases our application stack deployed using CloudFormation templates. This modular approach leverages AWS services and infrastructure as code principles to ensure scalability, resilience, and simplified deployment.
Our application is primarily made up of the following technologies.
./Yacrud-Stack/
├── Backend
│ ├── Networking Layer
│ ├── Cluster
│ ├── AWS RDS
│────────────────────────────────────── Week 10
│ ├── Fargate Service
│ └── AWS DynamoDB
├── Frontend CloudFront
├── CI/CD Services and Configuration
└────────────────────────────────────── Week 11Below are some of the main components and my own improvisation on the matter, based on my critical experience.
Networking
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): A dedicated VPC is established using CloudFormation, providing isolated network resources for the application.
- Ensuring the right CIDR block size is crucial , use this tool (opens in a new tab) to select an appropriate CIDR block.
- Public Subnet: Within the VPC, a public subnet is created, allowing external access to the application.
- Availability Zones: The architecture spans across multiple availability zones to enhance fault tolerance and ensure high availability.
Cluster
- Deployment: The cluster template is utilized to deploy a cluster, leveraging the VPC ID and Public Subnet from the Networking exports.
- Cluster Exports: Essential information such as the VPC ID, Service Security Group ID, and Target Groups are included in the Cluster Exports.
Frontend
- Integration: The Frontend template integrates with the cluster's Frontend Target Group, leveraging CloudFront for improved content delivery and scalability.
Backend Services
- Secure Communication: The Backend Services make use of the Cluster Exports' VPC ID to ensure secure communication within the VPC.
- Databases: An RDS database instance is included in the Backend Services for dealing with cruds and Dynamo for dealing with messages.
CI/CD
- Integration: Provision CodePipelines, and CodeBuild and configure the buildspec all using code.
CFN Network Layer
This CloudFormation template is designed to create foundational networking components for the app stack and assure cloud connectivity.
Refer to the CFN-AllArch. (opens in a new tab)
Some of the netowrk resources includes the following:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
VPC | Configures VPC with specified CIDR block and enables DNS hostnames for EC2 instances allows traffic only from IPv4 and disables IPv6. |
InternetGateway | Creates an Internet Gateway resource. |
RouteTable | Sets up a route table that enables routing to the Internet Gateway and local resources. It includes routes to the Internet Gateway and local destinations. |
Subnets | Creates six subnets, each associated explicitly with the route table. There are three public subnets (numbered 1 to 3) and three private subnets (numbered 1 to 3). |
As a good practice we can specify it in the template.yaml itself.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: |
This CloudFormation template establishes the essential networking components for your stack, ensuring a solid foundation.
It includes the following key components
- VPC
- configures DNS hostnames for EC2 instances
- only allows2 traffic from IPV4, IPV6 is disabled
- InternetGateway
- Route Table that enables routing to the InternetGateway and local resources
- route to the IGW
- route to Local
- Six subnets, each explicitly associated with the Route Table:
- 3 Public Subnets numbered 1 to 3
- 3 Private Subnets numbered 1 to 3The Template Parameters
VpcCidrBlock: Specifies the CIDR block for the VPC. The default value is10.0.0.0/16.Az1: Defines the Availability Zone for the first subnet. The default value isca-central-1a.SubnetCidrBlocks: Comma-delimited list of CIDR blocks for the private and public subnets. Please provide the CIDR blocks for all six subnets. Example:10.0.0.0/24, 10.0.4.0/24, 10.0.8.0/24, 10.0.12.0/24, 10.0.16.0/24, 10.0.20.0/24.Az2: Defines the Availability Zone for the second subnet. The default value isca-central-1b.Az3: Defines the Availability Zone for the third subnet. The default value isca-central-1d.
VpcCidrBlock:
Type: String
Default: 10.0.0.0/16
Az1:
Type: AWS::EC2::AvailabilityZone::Name
Default: ca-central-1a
SubnetCidrBlocks:
Description: "Comma-delimited list of CIDR blocks for our private public subnets"
Type: CommaDelimitedList
Default: >
10.0.0.0/24,
10.0.4.0/24,
10.0.8.0/24,
10.0.12.0/24,
10.0.16.0/24,
10.0.20.0/24
Az2:
Type: AWS::EC2::AvailabilityZone::Name
Default: ca-central-1b
Az3:
Type: AWS::EC2::AvailabilityZone::Name
Default: ca-central-1dVirtual Private Cloud
The VPC is a logically isolated section of the AWS cloud where you can launch AWS resources. It serves as the foundational networking component for Yarcrud app architecture, providing the network environment for all the other resources.
- Type:
AWS::EC2::VPC - Properties:
CidrBlock: Specifies the CIDR block for the VPC. You can reference the parameterVpcCidrBlock.EnableDnsHostnames: Enables DNS hostnames for EC2 instances.EnableDnsSupport: Enables DNS support.InstanceTenancy: Specifies the tenancy of the instances launched in the VPC (default value:default).Tags: Tags to assign to the VPC resource, including theNametag.
VPC:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPC
Properties:
CidrBlock: !Ref VpcCidrBlock
EnableDnsHostnames: true
EnableDnsSupport: true
InstanceTenancy: default
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}VPC"InternetGateway
The IGW enables internet connectivity for resources within the VPC, allowing your app to communicate with external services and users on the internet.
- Type:
AWS::EC2::InternetGateway - Properties:
Tags: Tags to assign to the internet gateway resource, including theNametag.
IGW:
Type: AWS::EC2::InternetGateway
Properties:
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}IGW"Attach VPC Gateway
Attaching the IGW to the VPC establishes the connectivity between your VPC and the internet, enabling inbound and outbound internet traffic for yacrud app.
- Type:
AWS::EC2::VPCGatewayAttachment - Properties:
VpcId: References the VPC resource.InternetGatewayId: References the InternetGateway resource.
AttachIGW:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPCGatewayAttachment
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
InternetGatewayId: !Ref IGWRoute Table
A route table contains a set of rules (routes) that determine where network traffic is directed within a VPC.
- Type:
AWS::EC2::RouteTable - Properties:
VpcId: References the VPC resource.Tags: Tags to assign to the route table resource, including theNametag.
RouteTable:
Type: AWS::EC2::RouteTable
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}RT"Route To Internet Gateway
This component defines a route in the route table to direct internet-bound traffic to the Internet Gateway to ensure that traffic destined for the internet is directed to the IGW.
- Type:
AWS::EC2::Route - DependsOn: Depends on the successful attachment of the InternetGateway to the VPC.
- Properties:
RouteTableId: References the RouteTable resource.GatewayId: References the InternetGateway resource.DestinationCidrBlock: Specifies the destination CIDR block for the route (0.0.0.0/0).
RouteToIGW:
Type: AWS::EC2::Route
DependsOn: AttachIGW
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref RouteTable
GatewayId: !Ref IGW
DestinationCidrBlock: 0.0.0.0/0Public Subnets
Public subnets are used to host our resources to have direct internet access and allow app to serve requests from the internet.
- Type:
AWS::EC2::Subnet - Properties:
AvailabilityZone: References the Availability Zone for each subnet.CidrBlock: References the appropriate CIDR block from theSubnetCidrBlocksparameter.EnableDns64: Disables DNS64 (IPv6).MapPublicIpOnLaunch: Specifies if a public IP is assigned to instances launched in the subnet.VpcId: References the VPC resource.Tags: Tags to assign to each subnet resource, including theNametag.
SubnetPub1:
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/aws-resource-ec2-subnet.html
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Ref Az1
CidrBlock: !Select [0, !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
EnableDns64: false
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true #public subnet
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetPub1"
SubnetPub2:
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/aws-resource-ec2-subnet.html
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Ref Az2
CidrBlock: !Select [1, !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
EnableDns64: false
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true #public subnet
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetPub2"
SubnetPub3:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Ref Az3
CidrBlock: !Select [2, !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
EnableDns64: false
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true #public subnet
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetPub3"Private Subnets
We used these private subnets to host resources that should not be directly accessible from the internet, such as RDS and DynamoDB connections.
- Type:
AWS::EC2::Subnet - Properties:
AvailabilityZone: References the Availability Zone for each subnet.CidrBlock: References the appropriate CIDR block from theSubnetCidrBlocksparameter.EnableDns64: Disables DNS64 (IPv6).MapPublicIpOnLaunch: Specifies if a public IP is assigned to instances launched in the subnet (set tofalsefor private subnets).VpcId: References the VPC resource.Tags: Tags to assign to each subnet resource, including theNametag
SubnetPriv1:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Ref Az1
CidrBlock: !Select [3, !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
EnableDns64: false
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: false #public subnet
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetPriv1"
SubnetPriv2:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Ref Az2
CidrBlock: !Select [4, !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
EnableDns64: false
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: false #public subnet
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetPriv2"
SubnetPriv3:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Ref Az3
CidrBlock: !Select [5, !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
EnableDns64: false
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: false #public subnet
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetPriv3"Subnet Associations
Subnet associations establish the link between subnets and the route table. Mainly, to control the flow of network traffic and ensure that it follows the desired routing paths within your VPC.
- Type:
AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation - Properties:
SubnetId: References theSubnetPubresource.RouteTableId: References theRouteTableresource.
SubnetPub1RTAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
SubnetId: !Ref SubnetPub1
RouteTableId: !Ref RouteTable
SubnetPub2RTAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
SubnetId: !Ref SubnetPub2
RouteTableId: !Ref RouteTable
SubnetPub3RTAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
SubnetId: !Ref SubnetPub3
RouteTableId: !Ref RouteTable
SubnetPriv1RTAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:Outputs
CloudFormation templates allow you to export certain values or resources for use in other stacks or AWS services.
- VpcId:
- Value: This output references the
VPCresource. - Export: The name of the export is generated using the
AWS::StackNameand appended withVpcId. For example, if the stack name isMyStack, the export name would be${AWS::StackName}VpcId.
- Value: This output references the
- SubnetCidrBlocks:
- Value: This output joins the
SubnetCidrBlocksparameter using a comma-separated format. - Export: The name of the export is generated using the
AWS::StackNameand appended withSubnetCidrBlocks. For example, if the stack name isMyStack, the export name would be${AWS::StackName}SubnetCidrBlocks.
- Value: This output joins the
- PublicSubnetIds:
- Value: This output joins the
SubnetPub1,SubnetPub2, andSubnetPub3resources using a comma-separated format. - Export: The name of the export is generated using the
AWS::StackNameand appended withPublicSubnetIds. For example, if the stack name isMyStack, the export name would be${AWS::StackName}PublicSubnetIds.
- Value: This output joins the
- PrivateSubnetIds:
- Value: This output joins the
SubnetPriv1,SubnetPriv2, andSubnetPriv3resources using a comma-separated format. - Export: The name of the export is generated using the
AWS::StackNameand appended withPrivateSubnetIds. For example, if the stack name isMyStack, the export name would be${AWS::StackName}PrivateSubnetIds.
- Value: This output joins the
Outputs:
VpcId:
Value: !Ref VPC
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}VpcId"
VpcCidrBlock:
Value: !GetAtt VPC.CidrBlock
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}VpcCidrBlock"
SubnetCidrBlocks:
Value: !Join [",", !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetCidrBlocks"
PublicSubnetIds:
Value: !Join
- ","
- - !Ref SubnetPub1
- !Ref SubnetPub2
- !Ref SubnetPub3
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}PublicSubnetIds"
PrivateSubnetIds:
Value: !Join
- ","
- - !Ref SubnetPriv1
- !Ref SubnetPriv2
- !Ref SubnetPriv3
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}PrivateSubnetIds"Availability Zones
- Value: This output joins the
Az1,Az2, andAz3parameters using a comma-separated format. - Export:
- Name: The name of the export is generated using the
AWS::StackNameand appended withAvailabilityZones. For example, if the stack name isMyStack, the export name would be${AWS::StackName}AvailabilityZones.
- Name: The name of the export is generated using the
AvailabilityZones:
Value: !Join
- ","
- - !Ref Az1
- !Ref Az2
- !Ref Az3
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}AvailabilityZones"The networking components we have covered form the foundation of our app's network layer.
❗Expand and apply the networking layer template.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: |
This YAML file defines the foundational networking components for our stack, including:
- VPC
- configures DNS hostnames for EC2 instances
- only allows2 traffic from IPV4, IPV6 is disabled
- InternetGateway
- Route Table that enables routing to the InternetGateway and local resources
- route to the IGW
- route to Local
- Six subnets, each explicitly associated with the Route Table:
- 3 Public Subnets numbered 1 to 3
- 3 Private Subnets numbered 1 to 3
Parameters:
VpcCidrBlock:
Type: String
Default: 10.0.0.0/16
Az1:
Type: AWS::EC2::AvailabilityZone::Name
Default: ca-central-1a
SubnetCidrBlocks:
Description: "Comma-delimited list of CIDR blocks for our private public subnets"
Type: CommaDelimitedList
Default: >
10.0.0.0/24,
10.0.4.0/24,
10.0.8.0/24,
10.0.12.0/24,
10.0.16.0/24,
10.0.20.0/24
Az2:
Type: AWS::EC2::AvailabilityZone::Name
Default: ca-central-1b
Az3:
Type: AWS::EC2::AvailabilityZone::Name
Default: ca-central-1d
Resources:
VPC:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPC
Properties:
CidrBlock: !Ref VpcCidrBlock
EnableDnsHostnames: true
EnableDnsSupport: true
InstanceTenancy: default
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}VPC"
IGW:
Type: AWS::EC2::InternetGateway
Properties:
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}IGW"
AttachIGW:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPCGatewayAttachment
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
InternetGatewayId: !Ref IGW
RouteTable:
Type: AWS::EC2::RouteTable
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}RT"
RouteToIGW:
Type: AWS::EC2::Route
DependsOn: AttachIGW
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref RouteTable
GatewayId: !Ref IGW
DestinationCidrBlock: 0.0.0.0/0
SubnetPub1:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Ref Az1
CidrBlock: !Select [0, !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
EnableDns64: false
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true #public subnet
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetPub1"
SubnetPub2:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Ref Az2
CidrBlock: !Select [1, !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
EnableDns64: false
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true #public subnet
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetPub2"
SubnetPub3:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Ref Az3
CidrBlock: !Select [2, !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
EnableDns64: false
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true #public subnet
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetPub3"
SubnetPriv1:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Ref Az1
CidrBlock: !Select [3, !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
EnableDns64: false
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: false
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetPriv1"
SubnetPriv2:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Ref Az2
CidrBlock: !Select [4, !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
EnableDns64: false
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: false
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetPriv2"
SubnetPriv3:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Ref Az3
CidrBlock: !Select [5, !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
EnableDns64: false
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: false
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetPriv3"
SubnetPub1RTAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
SubnetId: !Ref SubnetPub1
RouteTableId: !Ref RouteTable
SubnetPub2RTAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
SubnetId: !Ref SubnetPub2
RouteTableId: !Ref RouteTable
SubnetPub3RTAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
SubnetId: !Ref SubnetPub3
RouteTableId: !Ref RouteTable
SubnetPriv1RTAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
SubnetId: !Ref SubnetPriv1
RouteTableId: !Ref RouteTable
SubnetPriv2RTAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
SubnetId: !Ref SubnetPriv2
RouteTableId: !Ref RouteTable
SubnetPriv3RTAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
SubnetId: !Ref SubnetPriv3
RouteTableId: !Ref RouteTable
Outputs:
VpcId:
Value: !Ref VPC
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}VpcId"
VpcCidrBlock:
Value: !GetAtt VPC.CidrBlock
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}VpcCidrBlock"
SubnetCidrBlocks:
Value: !Join [",", !Ref SubnetCidrBlocks]
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}SubnetCidrBlocks"
PublicSubnetIds:
Value: !Join
- ","
- - !Ref SubnetPub1
- !Ref SubnetPub2
- !Ref SubnetPub3
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}PublicSubnetIds"
PrivateSubnetIds:
Value: !Join
- ","
- - !Ref SubnetPriv1
- !Ref SubnetPriv2
- !Ref SubnetPriv3
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}PrivateSubnetIds"
AvailabilityZones:
Value: !Join
- ","
- - !Ref Az1
- !Ref Az2
- !Ref Az3
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}AvailabilityZones"Save the template in aws/cfn/networking/template.yaml
Follow the below section to create a bucket prior your first deployement.
Deploy Networking Layer
- Create Script to deploy the template, It make use of TOML
#! /usr/bin/bash
set -e # stop execution if anything fails
abs_filepath="/workspace/aws-cloud-project-bootcamp/aws/cfn/networking/template.yaml"
FilePath=$(realpath --relative-base="$PWD" "$abs_filepath")
abs_config_filepath="/workspace/aws-cloud-project-bootcamp/aws/cfn/networking/config.toml"
ConfigFilePath=$(realpath --relative-base="$PWD" "$abs_config_filepath")
BUCKET=$(cfn-toml key deploy.bucket -t $ConfigFilePath)
REGION=$(cfn-toml key deploy.region -t $ConfigFilePath)
STACK_NAME=$(cfn-toml key deploy.stack_name -t $ConfigFilePath)
cfn-lint $FilePath
aws cloudformation deploy \
--stack-name $STACK_NAME \
--s3-bucket $BUCKET \
--s3-prefix networking \
--region $REGION \
--template-file "$FilePath" \
--no-execute-changeset \
--tags group=cruddur-networking \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM- save it in
bin/cfn/networkingand make it executable. - Create toml config.toml and add the required variables.
[deploy]
bucket = 'cfn-artifacts-111'
region = 'ca-central-1'
stack_name = 'CrdNet'- save the file in
aws/cfn/networking/config.toml - Deploy the template using
./bin/cfn/networking - Execute changeset from the console
Quickstart CFN Day! (opens in a new tab)
Setting Up CFN Artifact Bucket
As show in the stack architecture, CFN artifacts will be stored in a bucket.
Follow these steps to do so:
- Create an S3 bucket named
cfn-artifacts-111for the CFN artifact. This bucket will be used for all future templates.
aws s3 mb s3://cfn-artifacts-111- Save the bucket name in your development environment for future reference.
export CFN_BUCKET="cfn-artifacts-111"
gp env CFN_BUCKET="cfn-artifacts-111"We can now reference the bucket name in the scripts and get the artifacts on deployments in AWS.
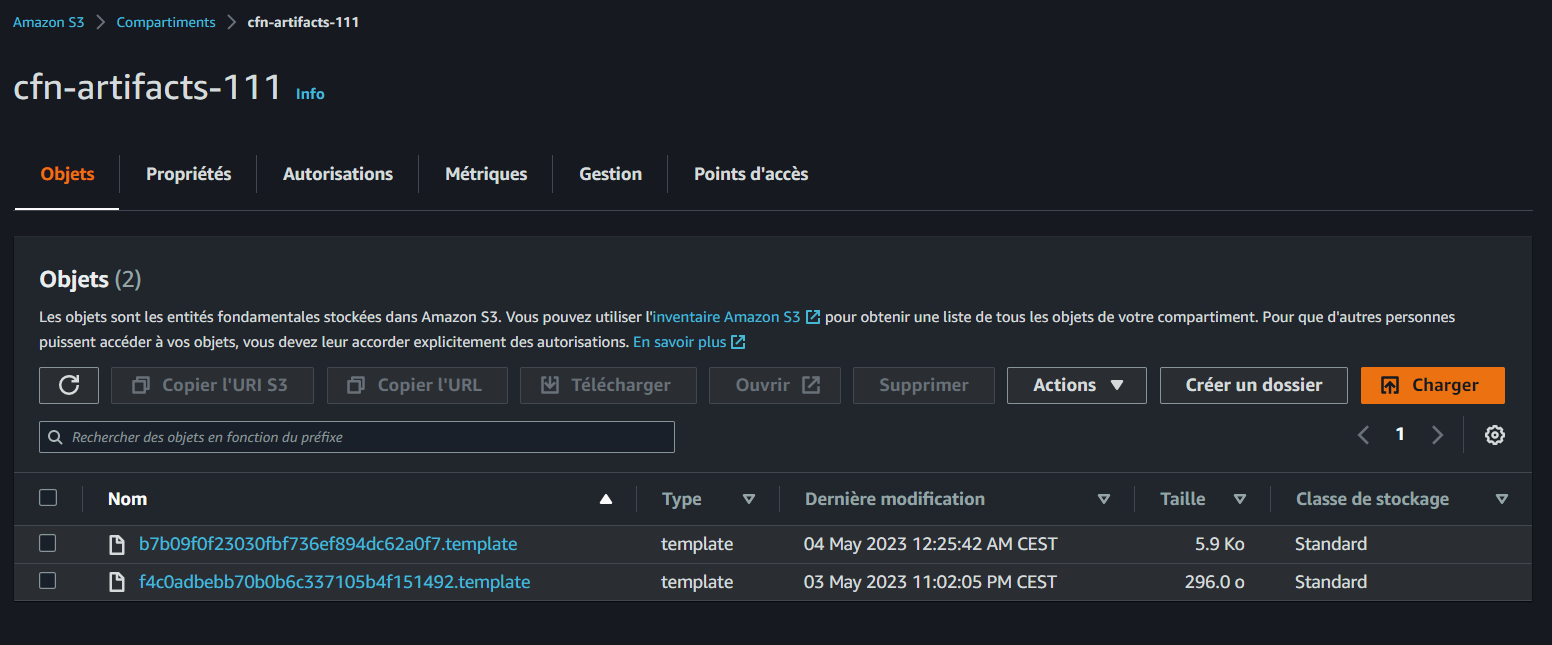
Bucket names are unique, you may not use mine.
Cluster Template
Create aws/cfn/cluster/config.toml and add the below variables.
[deploy]
bucket = 'cfn-artifacts-111'
region = '<region>'
stack_name = 'CrdCluster'
[parameters]
CertificateArn = 'arn:aws:acm:<region>:<aws-id>:certificate/dde234bf-7796-4c97-a977-b1d0a19e978d'
NetworkingStack = 'CrdNet'Cluster Description
Create aws/cfn/cluster/template.yaml and reflect on the description.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| ECS Fargate Cluster | Configures an ECS Fargate Cluster. |
| Application Load Balancer (ALB) | Sets up an ALB that is IPv4 only and internet-facing. |
| ALB Security Group | Defines a security group for the ALB. |
| Certificate (ACM) | Attaches a certificate from Amazon Certification Manager (ACM). |
| HTTPS Listener | Listens for HTTPS traffic and directs it to appropriate targets. |
| HTTP Listener | Listens for HTTP traffic and redirects it to HTTPS. |
| Backend Target Group | Routes traffic to the backend service. |
| Frontend Target Group | Routes traffic to the frontend service. |
Add the section to your Description in template.yaml
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: |
This template defines the networking and cluster configuration required to support Fargate containers. It includes:
- ECS Fargate Cluster
- Application Load Balanacer (ALB)
- ipv4 only
- internet facing
- ALB Security Group
- certificate attached from Amazon Certification Manager (ACM)
- HTTPS Listerner
- send naked domain to frontend Target Group
- send api. subdomain to backend Target Group
- HTTP Listerner
- redirects to HTTPS Listerner
- Backend Target Group
- Frontend Target GroupCluster Parameters
Parameters:
- NetworkingStack: This parameter represents the base layer of networking components, such as VPC and subnets. It allows you to specify the networking stack to use as the foundation for the Fargate cluster.
- CertificateArn: This parameter is of type string and is used to specify the ARN (Amazon Resource Name) of the certificate attached from Amazon Certification Manager (ACM). It allows you to associate an SSL/TLS certificate with the Application Load Balancer (ALB) for secure communication.
Parameters:
NetworkingStack:
Type: String
Description: This is our base layer of networking components eg. VPC, Subnets
Default: CrdNet
CertificateArn:
Type: StringCluster Frontend
- FrontendPort: This represents the port number for the frontend. The default value is set to 3000.
- FrontendHealthCheckIntervalSeconds: This specifies the interval, in seconds, between health checks for the frontend service. The default value is set to 15.
- FrontendHealthCheckPath: This represents the path that is used for the health check of the frontend service.
- FrontendHealthCheckPort: This defines the port that the ALB uses for health checks on the frontend service.
- FrontendHealthCheckProtocol: used for health checks on the frontend service. It specifies whether HTTP or HTTPS is used for the health check.
- FrontendHealthCheckTimeoutSeconds: determines how long the ALB waits for a response before considering the health check as failed.
- FrontendHealthyThresholdCount: Thisdefines the number of consecutive successful health checks required to consider the frontend service as healthy.
- FrontendUnhealthyThresholdCount: This specifies the number of consecutive failed health checks required to consider the frontend service as unhealthy.
FrontendPort:
Type: Number
Default: 3000
FrontendHealthCheckIntervalSeconds:
Type: Number
Default: 15
FrontendHealthCheckPath:
Type: String
Default: "/"
FrontendHealthCheckPort:
Type: String
Default: 80
FrontendHealthCheckProtocol:
Type: String
Default: HTTP
FrontendHealthCheckTimeoutSeconds:
Type: Number
Default: 5
FrontendHealthyThresholdCount:
Type: Number
Default: 2
FrontendUnhealthyThresholdCount:
Type: Number
Default: 2Cluster Backend
- BackendPort: This represents the port number for the backend and is set to 4567.
- BackendHealthCheckIntervalSeconds: Same applies as frontend.
- BackendHealthCheckPath: It specifies the endpoint that the ALB uses to check the health of the backend service and is set to
"/api/health-check". - BackendHealthCheckPort: This parameter is of type string and defines the port that the ALB uses
- BackendHealthCheckProtocol: It specifies whether HTTP or HTTPS is used for the health check. The default value is set to HTTP.
- BackendHealthCheckTimeoutSeconds: determines how long the ALB waits for a response before considering the health check as failed. The default value is set to 5.
- BackendHealthyThresholdCount: It specifies the minimum number of successful health checks needed to mark the service as healthy.
- BackendUnhealthyThresholdCount: This parameter is of type number and specifies the number of consecutive failed health checks required to consider the backend service as unhealthy.
BackendPort:
Type: Number
Default: 4567
BackendHealthCheckIntervalSeconds:
Type: String
Default: 15
BackendHealthCheckPath:
Type: String
Default: "/api/health-check"
BackendHealthCheckPort:
Type: String
Default: 80
BackendHealthCheckProtocol:
Type: String
Default: HTTP
BackendHealthCheckTimeoutSeconds:
Type: Number
Default: 5
BackendHealthyThresholdCount:
Type: Number
Default: 2
BackendUnhealthyThresholdCount:
Type: Number
Default: 2Cluster Required Resources
FargateCluster
The FargateCluster resource represents an ECS cluster using Fargate. It is the foundation of the containerized infrastructure. The properties for this resource include:
ClusterName: The name of the ECS cluster.CapacityProviders: The capacity providers to associate with the cluster. In this case, it is set toFARGATE.ClusterSettings: Additional settings for the cluster. Here, thecontainerInsightssetting is enabled.Configuration: Configuration settings for executing commands within the cluster, with theLoggingproperty set toDEFAULT.ServiceConnectDefaults: Default settings for Service Discovery namespaces within the cluster.
Resources:
FargateCluster:
Type: AWS::ECS::Cluster
Properties:
ClusterName: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}FargateCluster"
CapacityProviders:
- FARGATE
ClusterSettings:
- Name: containerInsights
Value: enabled
Configuration:
ExecuteCommandConfiguration:
Logging: DEFAULT
ServiceConnectDefaults:
Namespace: cruddurApplication Load Balancer
The ALB resource represents an Application Load Balancer. It acts as the entry point for incoming traffic and distributes it to the appropriate target groups. The properties for this resource include:
Name: The name of the load balancer.Type: The type of load balancer, set toapplication.IpAddressType: The IP address type for the load balancer, set toipv4.Scheme: The scheme of the load balancer, set tointernet-facing.SecurityGroups: The security groups associated with the load balancer.Subnets: The subnets in which the load balancer is deployed.LoadBalancerAttributes: Additional attributes for the load balancer, such as enabling HTTP/2, cross-zone load balancing, and more.
ALB:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::LoadBalancer
Properties:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}ALB"
Type: application
IpAddressType: ipv4
Scheme: internet-facing
SecurityGroups:
- !GetAtt ALBSG.GroupId
Subnets:
Fn::Split:
- ","
- Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub "${NetworkingStack}PublicSubnetIds"
LoadBalancerAttributes:
- Key: routing.http2.enabled
Value: true
- Key: routing.http.preserve_host_header.enabled
Value: false
- Key: deletion_protection.enabled
Value: true
- Key: load_balancing.cross_zone.enabled
Value: true
- Key: access_logs.s3.enabled
Value: falseHTTPS Listener
The HTTPSListener resource represents the HTTPS listener of the Application Load Balancer. It listens for incoming HTTPS traffic on port 443. The properties for this resource include:
Protocol: The protocol for the listener, set toHTTPS.Port: The port on which the listener listens.LoadBalancerArn: The ARN of the load balancer to which the listener is attached.Certificates: The SSL/TLS certificates associated with the listener.DefaultActions: The default actions to be performed when a request matches the listener.
HTTPSListener:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::Listener
Properties:
Protocol: HTTPS
Port: 443
LoadBalancerArn: !Ref ALB
Certificates:
- CertificateArn: !Ref CertificateArn
DefaultActions:
- Type: forward
TargetGroupArn: !Ref FrontendTGHTTP Listener
The HTTPListener resource represents the HTTP listener of the Application Load Balancer. It listens for incoming HTTP traffic on port 80 and redirects it to HTTPS. The properties for this resource include:
Protocol: The protocol for the listener, set toHTTP.Port: The port on which the listener listens.LoadBalancerArn: The ARN of the load balancer to which the listener is attached.DefaultActions: The default actions to be performed when a request matches the listener, in this case, a redirect to HTTPS.
HTTPListener:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::Listener
Properties:
Protocol: HTTP
Port: 80
LoadBalancerArn: !Ref ALB
DefaultActions:
- Type: redirect
RedirectConfig:
Protocol: "HTTPS"
Port: 443
Host: "#{host}"
Path: "/#{path}"
Query: "#{query}"
StatusCode: "HTTP_301"API ALB Listerner Rule
The ApiALBListernerRule resource represents a listener rule for the API subdomain. It defines conditions and actions for routing requests to the backend target group. The properties for this resource include:
Conditions: The conditions that must be met for the rule to be applied.Actions: The actions to be performed when a request matches the rule.ListenerArn: The ARN of the listener to which the rule belongs.Priority: The priority of the rule to determine its order of evaluation.
ApiALBListernerRule:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::ListenerRule
Properties:
Conditions:
- Field: host-header
HostHeaderConfig:
Values:
- api.cruddur.com
Actions:
- Type: forward
TargetGroupArn: !Ref BackendTG
ListenerArn: !Ref HTTPSListener
Priority: 1ALB Security Group
The ALBSG resource represents the security group associated with the Application Load Balancer. It controls the inbound and outbound traffic for the load balancer. The properties for this resource include:
GroupName: The name of the security group.GroupDescription: The description of the security group.VpcId: The ID of the VPC in which the security group resides.SecurityGroupIngress: The inbound rules for the security group, specifying the allowed protocols, ports, and source IP ranges.
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupName: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}AlbSG"
GroupDescription: Public Facing SG for our Cruddur ALB
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub ${NetworkingStack}VpcId
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: 443
ToPort: 443
CidrIp: '0.0.0.0/0'
Description: INTERNET HTTPS
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: 80
ToPort: 80
CidrIp: '0.0.0.0/0'
Description: INTERNET HTTPFargate Service Security Group
The ServiceSG resource represents the security group for the Fargate services. It controls the inbound and outbound traffic for the services. The properties for this resource include:
GroupName: The name of the security group.GroupDescription: The description of the security group.VpcId: The ID of the VPC in which the security group resides.SecurityGroupIngress: The inbound rules for the security group, specifying the allowed protocols, ports, and source security group.
ServiceSG:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupName: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}ServSG"
GroupDescription: Security for Fargate Services for Cruddur
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub ${NetworkingStack}VpcId
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
SourceSecurityGroupId: !GetAtt ALBSG.GroupId
FromPort: !Ref BackendPort
ToPort: !Ref BackendPort
Description: ALB HTTPBackend Target Group
The BackendTG resource represents the target group for the backend services. It defines the health checks and routing configuration for the services. The properties for this resource include:
BackendTG:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::TargetGroup
Properties:
Port: !Ref BackendPort
HealthCheckEnabled: true
HealthCheckProtocol: !Ref BackendHealthCheckProtocol
HealthCheckIntervalSeconds: !Ref BackendHealthCheckIntervalSeconds
HealthCheckPath: !Ref BackendHealthCheckPath
HealthCheckPort: !Ref BackendHealthCheckPort
HealthCheckTimeoutSeconds: !Ref BackendHealthCheckTimeoutSeconds
HealthyThresholdCount: !Ref BackendHealthyThresholdCount
UnhealthyThresholdCount: !Ref BackendUnhealthyThresholdCount
IpAddressType: ipv4
Matcher:
HttpCode: 200
Protocol: HTTP
ProtocolVersion: HTTP2
TargetType: ip
TargetGroupAttributes:
- Key: deregistration_delay.timeout_seconds
Value: 0
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub ${NetworkingStack}VpcId
Tags:
- Key: target-group-name
Value: backendFrontend Target Group
The FrontendTG resource represents the target group for the frontend services. It defines the health checks and routing configuration for the services.
FrontendTG:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::TargetGroup
Properties:
Port: !Ref FrontendPort
HealthCheckEnabled: true
HealthCheckProtocol: !Ref FrontendHealthCheckProtocol
HealthCheckIntervalSeconds: !Ref FrontendHealthCheckIntervalSeconds
HealthCheckPath: !Ref FrontendHealthCheckPath
HealthCheckPort: !Ref FrontendHealthCheckPort
HealthCheckTimeoutSeconds: !Ref FrontendHealthCheckTimeoutSeconds
HealthyThresholdCount: !Ref FrontendHealthyThresholdCount
UnhealthyThresholdCount: !Ref FrontendUnhealthyThresholdCount
IpAddressType: ipv4
Matcher:
HttpCode: 200
Protocol: HTTP
ProtocolVersion: HTTP2
TargetType: ip
TargetGroupAttributes:
- Key: deregistration_delay.timeout_seconds
Value: 0
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub ${NetworkingStack}VpcId
Tags:
- Key: target-group-name
Value: frontendCluster Outputs
Specify the output values for ClusterName, ServiceSecurityGroupId, ALBSecurityGroupId, FrontendTGArnand BackendTGArn.
Outputs:
ClusterName:
Value: !Ref FargateCluster
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}ClusterName"
ServiceSecurityGroupId:
Value: !GetAtt ServiceSG.GroupId
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}ServiceSecurityGroupId"
ALBSecurityGroupId:
Value: !GetAtt ALBSG.GroupId
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}ALBSecurityGroupId"
FrontendTGArn:
Value: !Ref FrontendTG
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}FrontendTGArn"
BackendTGArn:
Value: !Ref BackendTG
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}BackendTGArn"❗Expand and apply the entire Cluster template.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: |
This template defines the networking and cluster configuration required to support Fargate containers. It includes:
- ECS Fargate Cluster
- Application Load Balanacer (ALB)
- ipv4 only
- internet facing
- ALB Security Group
- certificate attached from Amazon Certification Manager (ACM)
- HTTPS Listerner
- send naked domain to frontend Target Group
- send api. subdomain to backend Target Group
- HTTP Listerner
- redirects to HTTPS Listerner
- Backend Target Group
- Frontend Target Group
Parameters:
NetworkingStack:
Type: String
Description: This is our base layer of networking components eg. VPC, Subnets
Default: CrdNet
CertificateArn:
Type: String
#Frontend ------
FrontendPort:
Type: Number
Default: 3000
FrontendHealthCheckIntervalSeconds:
Type: Number
Default: 15
FrontendHealthCheckPath:
Type: String
Default: "/"
FrontendHealthCheckPort:
Type: String
Default: 80
FrontendHealthCheckProtocol:
Type: String
Default: HTTP
FrontendHealthCheckTimeoutSeconds:
Type: Number
Default: 5
FrontendHealthyThresholdCount:
Type: Number
Default: 2
FrontendUnhealthyThresholdCount:
Type: Number
Default: 2
#Backend ------
BackendPort:
Type: Number
Default: 4567
BackendHealthCheckIntervalSeconds:
Type: String
Default: 15
BackendHealthCheckPath:
Type: String
Default: "/api/health-check"
BackendHealthCheckPort:
Type: String
Default: 80
BackendHealthCheckProtocol:
Type: String
Default: HTTP
BackendHealthCheckTimeoutSeconds:
Type: Number
Default: 5
BackendHealthyThresholdCount:
Type: Number
Default: 2
BackendUnhealthyThresholdCount:
Type: Number
Default: 2
Resources:
FargateCluster:
Type: AWS::ECS::Cluster
Properties:
ClusterName: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}FargateCluster"
CapacityProviders:
- FARGATE
ClusterSettings:
- Name: containerInsights
Value: enabled
Configuration:
ExecuteCommandConfiguration:
Logging: DEFAULT
ServiceConnectDefaults:
Namespace: cruddur
ALB:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::LoadBalancer
Properties:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}ALB"
Type: application
IpAddressType: ipv4
Scheme: internet-facing
SecurityGroups:
- !GetAtt ALBSG.GroupId
Subnets:
Fn::Split:
- ","
- Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub "${NetworkingStack}PublicSubnetIds"
LoadBalancerAttributes:
- Key: routing.http2.enabled
Value: true
- Key: routing.http.preserve_host_header.enabled
Value: false
- Key: deletion_protection.enabled
Value: true
- Key: load_balancing.cross_zone.enabled
Value: true
- Key: access_logs.s3.enabled
Value: false
HTTPSListener:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::Listener
Properties:
Protocol: HTTPS
Port: 443
LoadBalancerArn: !Ref ALB
Certificates:
- CertificateArn: !Ref CertificateArn
DefaultActions:
- Type: forward
TargetGroupArn: !Ref FrontendTG
HTTPListener:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::Listener
Properties:
Protocol: HTTP
Port: 80
LoadBalancerArn: !Ref ALB
DefaultActions:
- Type: redirect
RedirectConfig:
Protocol: "HTTPS"
Port: 443
Host: "#{host}"
Path: "/#{path}"
Query: "#{query}"
StatusCode: "HTTP_301"
ApiALBListernerRule:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::ListenerRule
Properties:
Conditions:
- Field: host-header
HostHeaderConfig:
Values:
- api.cruddur.com
Actions:
- Type: forward
TargetGroupArn: !Ref BackendTG
ListenerArn: !Ref HTTPSListener
Priority: 1
ALBSG:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupName: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}AlbSG"
GroupDescription: Public Facing SG for our Cruddur ALB
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub ${NetworkingStack}VpcId
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: 443
ToPort: 443
CidrIp: '0.0.0.0/0'
Description: INTERNET HTTPS
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: 80
ToPort: 80
CidrIp: '0.0.0.0/0'
Description: INTERNET HTTP
ServiceSG:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupName: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}ServSG"
GroupDescription: Security for Fargate Services for Cruddur
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub ${NetworkingStack}VpcId
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
SourceSecurityGroupId: !GetAtt ALBSG.GroupId
FromPort: !Ref BackendPort
ToPort: !Ref BackendPort
Description: ALB HTTP
BackendTG:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::TargetGroup
Properties:
Port: !Ref BackendPort
HealthCheckEnabled: true
HealthCheckProtocol: !Ref BackendHealthCheckProtocol
HealthCheckIntervalSeconds: !Ref BackendHealthCheckIntervalSeconds
HealthCheckPath: !Ref BackendHealthCheckPath
HealthCheckPort: !Ref BackendHealthCheckPort
HealthCheckTimeoutSeconds: !Ref BackendHealthCheckTimeoutSeconds
HealthyThresholdCount: !Ref BackendHealthyThresholdCount
UnhealthyThresholdCount: !Ref BackendUnhealthyThresholdCount
IpAddressType: ipv4
Matcher:
HttpCode: 200
Protocol: HTTP
ProtocolVersion: HTTP2
TargetType: ip
TargetGroupAttributes:
- Key: deregistration_delay.timeout_seconds
Value: 0
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub ${NetworkingStack}VpcId
Tags:
- Key: target-group-name
Value: backend
FrontendTG:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::TargetGroup
Properties:
Port: !Ref FrontendPort
HealthCheckEnabled: true
HealthCheckProtocol: !Ref FrontendHealthCheckProtocol
HealthCheckIntervalSeconds: !Ref FrontendHealthCheckIntervalSeconds
HealthCheckPath: !Ref FrontendHealthCheckPath
HealthCheckPort: !Ref FrontendHealthCheckPort
HealthCheckTimeoutSeconds: !Ref FrontendHealthCheckTimeoutSeconds
HealthyThresholdCount: !Ref FrontendHealthyThresholdCount
UnhealthyThresholdCount: !Ref FrontendUnhealthyThresholdCount
IpAddressType: ipv4
Matcher:
HttpCode: 200
Protocol: HTTP
ProtocolVersion: HTTP2
TargetType: ip
TargetGroupAttributes:
- Key: deregistration_delay.timeout_seconds
Value: 0
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub ${NetworkingStack}VpcId
Tags:
- Key: target-group-name
Value: frontend
Outputs:
ClusterName:
Value: !Ref FargateCluster
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}ClusterName"
ServiceSecurityGroupId:
Value: !GetAtt ServiceSG.GroupId
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}ServiceSecurityGroupId"
ALBSecurityGroupId:
Value: !GetAtt ALBSG.GroupId
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}ALBSecurityGroupId"
FrontendTGArn:
Value: !Ref FrontendTG
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}FrontendTGArn"
BackendTGArn:
Value: !Ref BackendTG
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}BackendTGArn"Create bin/cfn/cluster script and make it executable.
#! /usr/bin/bash
set -e
abs_template_filepath="/workspace/aws-cloud-project-bootcamp/aws/cfn/cluster/template.yaml"
TemplateFilePath=$(realpath --relative-base="$PWD" "$abs_template_filepath")
abs_config_filepath="/workspace/aws-cloud-project-bootcamp/aws/cfn/cluster/config.toml"
ConfigFilePath=$(realpath --relative-base="$PWD" "$abs_config_filepath")
BUCKET=$(cfn-toml key deploy.bucket -t $ConfigFilePath)
REGION=$(cfn-toml key deploy.region -t $ConfigFilePath)
STACK_NAME=$(cfn-toml key deploy.stack_name -t $ConfigFilePath)
PARAMETERS=$(cfn-toml params v2 -t $ConfigFilePath)
cfn-lint $TemplateFilePath
aws cloudformation deploy \
--stack-name "$STACK_NAME" \
--s3-bucket "$BUCKET" \
--s3-prefix cluster \
--region $REGION \
--template-file $TemplateFilePath \
--no-execute-changeset \
--tags group=cruddur-cluster \
--parameter-overrides $PARAMETERS \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM- Deploy the template using
./bin/cfn/cluster
- From the console Execute the changeset.
AWS RDS Template
Create aws/cfn/db/config.toml and add the below variables.
[deploy]
bucket = 'cfn-artifacts-111'
region = '<region>'
stack_name = 'CrdDb'
[parameters]
NetworkingStack = 'CrdNet'
ClusterStack = 'CrdDb'
MasterUsername = 'cruddurroot'Create aws/cfn/db/template.yaml and start developing.
Describing the template
This is the cfn for the primary Postgres RDS Database for crud function.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: |
The primary Postgres RDS Database for the application
- RDS Instance
- Database Security GroupParameters
NetworkingStack: This parameter represents the base layer of networking components, such as VPC and subnets.ClusterStack: This parameter represents the Fargate cluster.BackupRetentionPeriod: This parameter specifies the number of days to retain automated backups.DBInstanceClass: This parameter defines the compute and memory capacity for the database instance.
Parameters:
NetworkingStack:
Type: String
Description: This is our base layer of networking components eg. VPC, Subnets
Default: CrdNet
ClusterStack:
Type: String
Description: This is our FargateCluster
Default: CrdCluster
BackupRetentionPeriod:
Type: Number
Default: 0
DBInstanceClass:
Type: String
Default: db.t4g.microDBInstanceIdentifier: This parameter specifies the identifier for the database instance.DBName: This parameter specifies the name of the database.DeletionProtection: This parameter indicates whether deletion protection is enabled or not.EngineVersion: This parameter specifies the version number of the database engine.MasterUsername: This parameter specifies the master username for the database instance.MasterUserPassword: This parameter specifies the master user password for the database instance.
DBInstanceIdentifier:
Type: String
Default: cruddur-instance
DBName:
Type: String
Default: cruddur
DeletionProtection:
Type: String
AllowedValues:
- true
- false
Default: true
EngineVersion:
Type: String
Default: '15.2'
MasterUsername:
Type: String
MasterUserPassword:
Type: String
NoEcho: truePostgreSQL Resource
- Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
- Description: Public Facing SG for our Cruddur ALB
- Properties:
GroupName: The name of the security group.GroupDescription: The description of the security group.VpcId: The ID of the VPC.SecurityGroupIngress: Ingress rules for the security group.
# Start Resource Section
Resources:
RDSPostgresSG:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupName: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}RDSSG"
GroupDescription: Public Facing SG for our Cruddur ALB
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub ${NetworkingStack}VpcId
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
SourceSecurityGroupId:
Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub ${ClusterStack}ServiceSecurityGroupId
FromPort: 5432
ToPort: 5432
Description: ALB HTTPPosgreSQL Subnet Group
- Type: AWS::RDS::DBSubnetGroup
- Properties:
DBSubnetGroupName: The name of the DB subnet group.DBSubnetGroupDescription: The description of the DB subnet group.SubnetIds: IDs of the subnets in the DB subnet group.
DBSubnetGroup:
Type: AWS::RDS::DBSubnetGroup
Properties:
DBSubnetGroupName: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}DBSubnetGroup"
DBSubnetGroupDescription: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}DBSubnetGroup"
SubnetIds: { 'Fn::Split' : [ ',' , { "Fn::ImportValue": { "Fn::Sub": "${NetworkingStack}PublicSubnetIds" }}] }Database
- Type: AWS::RDS::DBInstance
- Properties:
AllocatedStorage: The amount of storage to allocate to the database instance.AllowMajorVersionUpgrade: Indicates whether major version upgrades are allowed.AutoMinorVersionUpgrade: Indicates whether minor version upgrades are applied automatically.BackupRetentionPeriod: The number of days to retain automated backups.DBInstanceClass: The compute and memory capacity for the database instance.DBInstanceIdentifier: The identifier for the database instance.
Database:
Type: AWS::RDS::DBInstance
DeletionPolicy: 'Snapshot'
UpdateReplacePolicy: 'Snapshot'
Properties:
AllocatedStorage: '20'
AllowMajorVersionUpgrade: true
AutoMinorVersionUpgrade: true
BackupRetentionPeriod: !Ref BackupRetentionPeriod
DBInstanceClass: !Ref DBInstanceClass
DBInstanceIdentifier: !Ref DBInstanceIdentifier- DB Connection Properties:
DBName: The name of the database.DBSubnetGroupName: The name of the DB subnet group to associate with the database instance.DeletionProtection: Indicates whether deletion protection is enabled.EnablePerformanceInsights: Indicates whether Performance Insights is enabled.Engine: The name of the database engine.EngineVersion: The version number of the database engine.MasterUsername: The master username for the database instance.MasterUserPassword: The master user password for the database instance.PubliclyAccessible: Indicates whether the database instance is publicly accessible.VPCSecurityGroups: Security groups associated with the database instance.
DBName: !Ref DBName
DBSubnetGroupName: !Ref DBSubnetGroup
DeletionProtection: !Ref DeletionProtection
EnablePerformanceInsights: true
Engine: postgres
EngineVersion: !Ref EngineVersion
# Must be 1 to 63 letters or numbers.
# First character must be a letter.
# Can't be a reserved word for the chosen database engine.
MasterUsername: !Ref MasterUsername
# Constraints: Must contain from 8 to 128 characters.
MasterUserPassword: !Ref MasterUserPassword
PubliclyAccessible: true
VPCSecurityGroups:
- !GetAtt RDSPostgresSG.GroupId❗Expand and apply the entire RDS Databse template.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: |
The primary Postgres RDS Database for the application
- RDS Instance
- Database Security Group
Parameters:
NetworkingStack:
Type: String
Description: This is our base layer of networking components eg. VPC, Subnets
Default: CrdNet
ClusterStack:
Type: String
Description: This is our FargateCluster
Default: CrdCluster
BackupRetentionPeriod:
Type: Number
Default: 0
DBInstanceClass:
Type: String
Default: db.t4g.micro
DBInstanceIdentifier:
Type: String
Default: cruddur-instance
DBName:
Type: String
Default: cruddur
DeletionProtection:
Type: String
AllowedValues:
- true
- false
Default: true
EngineVersion:
Type: String
Default: '15.2'
MasterUsername:
Type: String
MasterUserPassword:
Type: String
NoEcho: true
Resources:
RDSPostgresSG:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupName: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}RDSSG"
GroupDescription: Public Facing SG for our Cruddur ALB
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub ${NetworkingStack}VpcId
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
SourceSecurityGroupId:
Fn::ImportValue:
!Sub ${ClusterStack}ServiceSecurityGroupId
FromPort: 5432
ToPort: 5432
Description: ALB HTTP
DBSubnetGroup:
Type: AWS::RDS::DBSubnetGroup
Properties:
DBSubnetGroupName: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}DBSubnetGroup"
DBSubnetGroupDescription: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}DBSubnetGroup"
SubnetIds: { 'Fn::Split' : [ ',' , { "Fn::ImportValue": { "Fn::Sub": "${NetworkingStack}PublicSubnetIds" }}] }
Database:
Type: AWS::RDS::DBInstance
DeletionPolicy: 'Snapshot'
UpdateReplacePolicy: 'Snapshot'
Properties:
AllocatedStorage: '20'
AllowMajorVersionUpgrade: true
AutoMinorVersionUpgrade: true
BackupRetentionPeriod: !Ref BackupRetentionPeriod
DBInstanceClass: !Ref DBInstanceClass
DBInstanceIdentifier: !Ref DBInstanceIdentifier
DBName: !Ref DBName
DBSubnetGroupName: !Ref DBSubnetGroup
DeletionProtection: !Ref DeletionProtection
EnablePerformanceInsights: true
Engine: postgres
EngineVersion: !Ref EngineVersion
MasterUsername: !Ref MasterUsername
MasterUserPassword: !Ref MasterUserPassword
PubliclyAccessible: true
VPCSecurityGroups:
- !GetAtt RDSPostgresSG.GroupIdCreate bin/cfn/db script and make it executable.
#! /usr/bin/env bash
set -e # stop the execution of the script if it fails
CFN_PATH="/workspace/aws-cloud-project-bootcamp/aws/cfn/db/template.yaml"
CONFIG_PATH="/workspace/aws-cloud-project-bootcamp/aws/cfn/db/config.toml"
echo $CFN_PATH
cfn-lint $CFN_PATH
BUCKET=$(cfn-toml key deploy.bucket -t $CONFIG_PATH)
REGION=$(cfn-toml key deploy.region -t $CONFIG_PATH)
STACK_NAME=$(cfn-toml key deploy.stack_name -t $CONFIG_PATH)
PARAMETERS=$(cfn-toml params v2 -t $CONFIG_PATH)
aws cloudformation deploy \
--stack-name $STACK_NAME \
--s3-bucket $BUCKET \
--s3-prefix db \
--region $REGION \
--template-file "$CFN_PATH" \
--no-execute-changeset \
--tags group=cruddur-db \
--parameter-overrides $PARAMETERS MasterUserPassword=$DB_PASSWORD \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM- Deploy the template using
./bin/cfn/db
- From the console Execute the changeset.
Consult additional IaC workload Incl CFN, SAM, TF and more for the following Week Eleven.
Reference
- CFN Template basics YAML VS JSON (opens in a new tab)
- Paloalto Networks Policy as Code (opens in a new tab)
- Cloud security posture management (opens in a new tab)
- OWASP IaC Security Cheatsheet (opens in a new tab)
- Tom's Obvious, Minimal Language Project (opens in a new tab)
- NetDevOps modern approach to networking deployments (opens in a new tab)
- Ashish Security Podcast (opens in a new tab)
Week 10 Of AWS Cloud Project Bootcamp — Office Hours Checklist (opens in a new tab)